
CALEC completely restored the cornea in 50% of participants at their 3-month visit and that rate of complete success increased to 79% and 77% at their 12- and 18-month visits, respectively.

CALEC completely restored the cornea in 50% of participants at their 3-month visit and that rate of complete success increased to 79% and 77% at their 12- and 18-month visits, respectively.
Current studies are using a polygenic risk score to evaluate the risk and clinical outcomes in primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG).

The study is aiming to gain insight into glaucoma in African American populations.
Researchers are exploring gene-independent therapeutic strategies to circumvent the challenges of gene-replacement therapies.

Investigators find approach improved vision and visual fields in some patients.

RGX-314 may be a promising therapeutic option for exudative AMD.

Preliminary results have shown that AGTC-401 and AGTC-402 seem safe and well tolerated in patients with ACHM.
In a presentation at ARVO, Friederike Kortuem, MD, MSc, explains that treatment with voretigene neparvovec-rzyl led to a short-term change in the foveal morphology in a patient with visual impairment that included nyctalopia and decreased visual acuity in early childhood.

Investigators used an adeno-associated viral vector to deliver a normal functioning copy of the RPGR gene via subretinal injection.

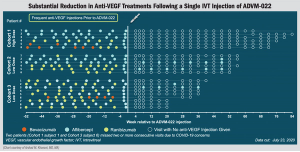
A non-viral gene therapy sustained drug-delivery product that delivers anti-VEGF to the eye may replace the need for repeated intravitreal anti-VEGF injections and improve vision in patients with wet AMD.

Approach can unravel causes in MYOC and TBK1 glaucoma.

Studying zebrafish helps unravel the mysteries of photoreceptor regeneration.

Studies are uncovering a range of potential treatment options for disorders.
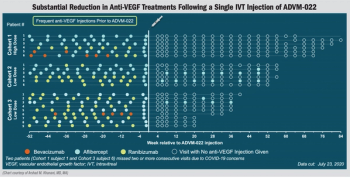
Investigators observe dramatic decrease in treatment burden seen in OPTIC study.

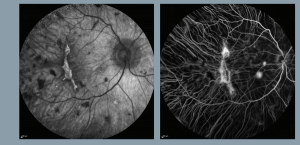
Treatment may facilitate sight in end-stage retinitis pigmentosa.
Study examining the role of IL-17A in patients with diabetes.
Investigators focus on biophysical method to study protein-protein interactions .
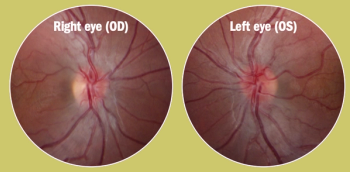
A new gene therapy for this patient population targets the ND4 gene mutation.
Nine pediatric patients with Leber congenital amaurosis show visual improvement in clinical trials.

With several clinical trials underway, ocular therapy is seen as having potential in the treatment of a number of gene-related diseases.
Intravitreal gene therapy continues to be well tolerated and shows robust efficacy

Investigators find that nanoparticles deliver gene therapy successfully in mice, rats.
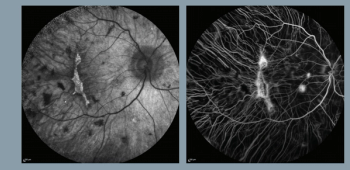
Gene therapy to treat choroideremia shows potential for maintaining or improving vision
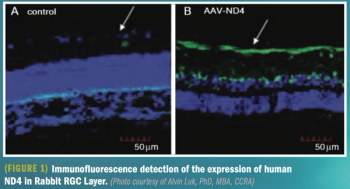
Intravitreal injection offers safety, efficacy, and improved vision in patients


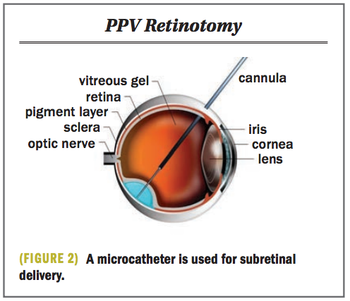
Published: November 29th 2021 | Updated:
Published: January 28th 2020 | Updated:
Published: March 16th 2021 | Updated:
Published: August 11th 2020 | Updated:
Published: October 21st 2020 | Updated:

Published: January 29th 2020 | Updated: