
CAR T cells are a more effective therapy if manufactured for patients with multiple myeloma prior to the onset of relapsed or refractory disease.

CAR T cells are a more effective therapy if manufactured for patients with multiple myeloma prior to the onset of relapsed or refractory disease.
Delays in CAR T-cell therapy may significantly decrease gains in survival and productivity for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
A new study looked at the rates of response and remission in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma who underwent CD19-directed CAR-T cell therapy.
Researchers tested radiation therapy as a bridging therapy for patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma during the interval between T-cell collection and final CAR T administration.

Researchers tested the addition of the T cell–boosting decitabine to anti–PD-1 therapy with camrelizumab among patients with relapsed or refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma.

Researchers have identified a potential new target for CAR T-cell therapy in patients with multiple myeloma.
The PRECIS study looked at consolidation treatment with autologous stem cell transplantation vs whole-brain radiation therapy in younger patients with CNS lymphoma.
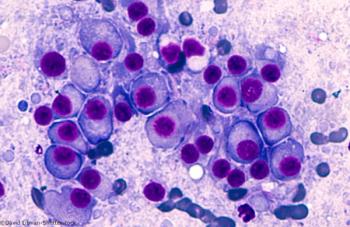
A phase I study examines the use of LCAR-B38M, a CAR T-cell therapy directed against BCMA, in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
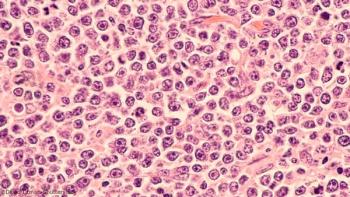
Antiretroviral therapy and rituximab show promise in aids-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients.

CAR T-cell therapy with bb2121 induced deep, long-lasting responses in patients with heavily pretreated MM.

The approval includes adults with R/R DLBCL after two or more lines of prior systemic therapy, high-grade B-cell lymphoma, and DLBCL arising from FL.

The US FDA has granted Priority Review designation for tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) for treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who are ineligible for, or have relapsed after, ASCT.

A single infusion of the anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy tisagenlecleucel produced durable remissions in pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic lymphoma.

The FDA has expanded the label for cabozantinib (Cabometyx) to include first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma regardless of treatment status. Cabozantinib was initially approved in patients who had previously received anti-angiogenic therapy.

CAR T cells targeting CD19 can be effective at treating relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma or follicular lymphoma, with high rates of durable remission.

A single treatment with a second-generation CAR T-cell treatment elicited an overall response rate of 94% in a small study of patients with heavily pretreated multiple myeloma, according to the results of a phase I study presented at the ASH Annual Meeting.
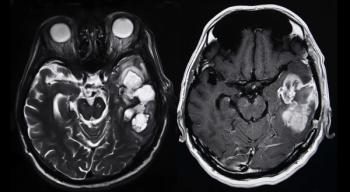
More than 25% of patients with recurrent, high-grade glioma treated with a gene therapy combination were alive more than 3 years after treatment, according to data from a subset of patients in a phase I clinical trial.

Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified T-cell therapy was highly effective in patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia who had previously failed treatment with ibrutinib.

The FDA has approved the first gene therapy available in the United States, tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), for the treatment of pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

Patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma treated with lenalidomide maintenance therapy after undergoing autologous stem-cell transplantation had significantly improved overall survival compared with observation or placebo.

Adult patients with early thymic precursor (ETP) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), a subgroup of T-cell ALL, could benefit from the use of response-based risk stratification and therapy intensification similar to that used in pediatric patients with ETP-ALL.

Pazopanib 600 mg daily as adjuvant therapy did not prolong disease-free survival for patients with locally advanced renal cell carcinoma.

CAR T-cell therapy targeting B-cell maturation protein may be a new effective type of immunotherapy treatment for patients with multiple myeloma.

More than one-third of patients with metastatic uveal melanoma had objective tumor regression when treated with adoptive transfer of autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.

Administration of autologous HER2-specific CAR-modified virus specific T Cells was safe and had clinical benefit for some patients with progressive glioblastoma, a disease with limited effective therapeutic options.

Low pretreatment disease burden improved durability of CAR T-cell therapy in patients with relapsed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

The use of anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells induced a nearly sixfold higher rate of complete response compared with historical outcomes in patients with refractory, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

T-cell therapy targeting CD22, a protein found on the surface of leukemic cells, was safe and feasible in a small and ongoing study of patients with ALL.

Administration of bb2121, a novel anti–B-cell maturation antigen CAR T-cell therapy, produced anti-tumor responses in heavily pretreated patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, according to interim data from a phase I trial.

Longer durations of maintenance therapy with lenalidomide were associated with longer survival among patients who underwent autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant for multiple myeloma.

Published: April 20th 2017 | Updated:
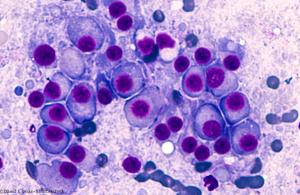
Published: January 24th 2019 | Updated:

Published: August 17th 2017 | Updated:
Published: July 18th 2014 | Updated:

Published: December 14th 2016 | Updated:

Published: February 8th 2018 | Updated: