
AZD0120, a dual-targeted CAR T-cell therapy, shows high efficacy in treating relapsed multiple myeloma, achieving a 96% response rate.

Silas Inman joined MJH Life Sciences in early 2011 and has evolved his role at the organization throughout his tenure at MJH. At various points, Silas has been accountable for several organic launches of highly successful brands, including Targeted Oncology™ and NeurologyLive®, and for quickly transforming acquisitions into high-functioning business units. Prior to joining MJH, Silas, who attended Eastern Michigan University, was an EMT, frontend web developer, and social media/SEO expert. Follow him on X @SilasInman or email him at [email protected].

AZD0120, a dual-targeted CAR T-cell therapy, shows high efficacy in treating relapsed multiple myeloma, achieving a 96% response rate.

Ciltacabtagene autoleucel significantly enhances survival rates in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, outperforming standard treatments across various patient subgroups.

KITE-363 shows promising results in treating relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma, with high response rates and manageable adverse events.

Arlocabtagene autoleucel shows promise as a potential first in class GPRC5D-targeted CAR T-cell therapy for heavily pretreated multiple myeloma.

In the wake of fludarabine shortages, lemphodepletion with bendamustine was found to be an effective alternative compared for patients with large B-cell lymphoma being treated with a CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy.

With an FDA deadline pending in January, tabelecleucel remained safe and effective with longer follow-up for Epstein–Barr virus-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease.

Zamtocabtagene autoleucel showed promising early complete response rates and survival outcomes in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.

Rapcabtagene autoleucel showed high rates of durable complete remissions and a favorable safety profile for patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.

The CAR T-cell therapy AIC100 demonstrated promising responses and a low level of toxicity in patients with advanced thyroid cancer.

BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy anitocabtagene autoleucel demonstrated a 76% complete remission rate and 89% negative minimal residual disease in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.

A CRISPR/Cas9-edited allogeneic stem cell transplantation effectively reduced hematopoietic toxicity associated with maintenance gemtuzumab ozogamicin for high-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML).

CD19-directed CAR-T-cell therapy resulted in sustained remission for over a year and no return of autoimmunity for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, idiopathic inflammatory myositis, and systemic sclerosis.

Long-term data on lovo-cel gene therapy for sickle cell disease (SCD) reveals sustained efficacy at 60 months.

Patient preferences should be considered when selecting the optimal treatment regimen for patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma, as both CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapies and CD20-targeted bispecific antibodies can be efficacious.
A final analysis of data from CARTITUDE-1 was also presented at SOHO 2023, which revealed a PFS of 24.9 months in treated patients.
Second-line lisocabtagene maraleucel reduced the risk of an event occurring by 64.4% compared with standard-of-care chemoimmunotherapy induction and autologous stem cell transplantation.
Annualized bleeding rates were superior with the gene therapy fidanacogene elaparvovec compared with factor IX treatment for patients with moderately severe to severe hemophilia B.
The 5-year relapse-free survival rate was 22.3% with T-VEC prior to surgery, compared with 15.2% for surgery alone.
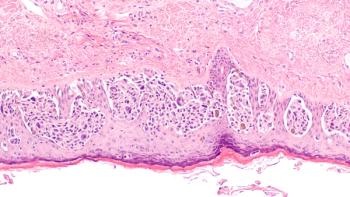
Based on the findings, investigators are considering registration with the FDA and EMA.
Findings from the US-based study align with results from a phase 1b/2 study completed in China of CT041 in patients with gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.

Updated data at ARVO show that AGTC-501 had sustained efficacy and safety at 18 months for patients with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa caused by RPGR mutations.
SQZ-PBMC-HPV receives FDA Fast Track Designation for patients with advanced or metastatic HPV16+ solid tumors, following promising early results.
Pivotal phase 3 findings for ofra-vec in patients with ovarian cancer are anticipated in the second half of 2022.
NKX101 and NKX019 have demonstrated preliminary signs of safety and efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with AML and NHL in 2 separate phase 1 studies.
KUR-502 elicited promising response rates for patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies in a phase 1 study.
The FDA has granted a Fast Track Designation to GCC19CART as a potential treatment for adult patients with relapsed and refractory metastatic colorectal cancer.
ADI-001 has been granted a Fast Track Designation by the FDA a potential treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The gene therapy ASC618 has received European and US designations and opinions that could help expedite development for hemophilia A.
This designation follows a fast track designation and IND application approval for the agent.

The designation follows the approval of its IND application for the natural killer cell therapy in November 2021.

Published: December 7th 2024 | Updated:

Published: March 26th 2021 | Updated:

Published: April 22nd 2021 | Updated:

Published: March 25th 2021 | Updated:

Published: March 10th 2021 | Updated:

Published: December 12th 2023 | Updated: