Results of the phase 1 portion of ZUMA-4 support continued investigation into the efficacy of KTE-X19 in pediatric patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

Results of the phase 1 portion of ZUMA-4 support continued investigation into the efficacy of KTE-X19 in pediatric patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

Long-term efficacy assessment of brexucabtagene autoleucel demonstrated high rates of MRD negativity and CR rates in pediatric and adolescent patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

Intensified induction therapy with daratumumab in addition to cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone and bortezomib-augmented autologous stem cell transplant yielded robust responses in patients with ultra¬ high–risk multiple myeloma or primary plasma cell leukemia
The CAR T-cell therapy lisocabtagene maraleucel resulted in better efficacy versus standard of care with no new safety signals.
Based on data from the CARTITUDE-1, the BCMA-targeting CAR T-cell therapy ciltacabtagene autoleucel moves forward towards regulatory approval in multiple myeloma.
An off-the-shelf cellular therapy that combines Epstein Barr Virus–Specific T cells and a CD30-targeting chimeric antigen receptor product demonstrated safety and early efficacy in a group of patients with CD30-positive lymphomas.
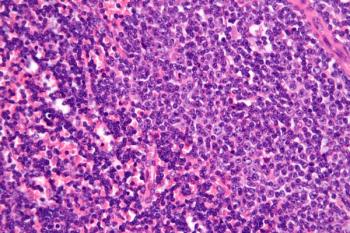
MB-106, a CD20-targeted CAR T-cell therapy that has shown promise in the treatment of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, is now being considered for patients with relapsed or refractory CD20-positive chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
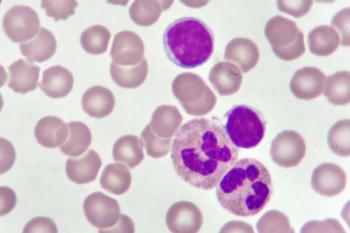
CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy brexucabtagene autoleucel will be considered by FDA for indication in adults with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

Follow-up of 4.8 years to a phase 1 trial demonstrated that deep and durable responses are attainable in a large cohort of children and young adult patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia who were treated with CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy followed by allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.

Data from the phase 2 ZUMA-5 trial supported the approval of axicabtagene ciloleucel, a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, as a treatment for patients with follicular lymphoma in the third-line setting.

December 5, 2020 - Patients with heavily pretreated multiple myeloma maintained durable responses with the chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy idecabtagene vicleucel in updated findings presented from the phase 1 CRB-401 trial.

Patients with chemotherapy-naïve, locally advanced or metastatic non–small cell lung cancer who were treated in the phase 2 CITYSCAPE trial with tiragolumab, an inhibitor of the immunomodulatory receptor TIGIT, plus and anti–PD-L1 agent demonstrated better efficacy versus single-agent checkpoint inhibitor therapy alone.

The first-in-clinic universal CAR T-cell therapy TruUCAR GC027 induced promising early response rates and demonstrated a manageable safety profile with no evidence of neurotoxicity events or graft-versus-host disease in adult patients with relapsed/refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

Patients with pretreated non–small cell lung cancer and EGFR exon 20 insertions demonstrated a 68.7% disease control rate while on poziotinib systemic therapy.

An “off-the-shelf” Epstein Barr-virus–specific cytotoxic lymphocyte CAR product derived from cells harvested from third-party donors induced a 100% response rate in adult and pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

Outpatient administration of CAR T-Cell therapy is safe and effective, according to an analysis of 3 studies of lisocabtagene maraleucel in patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma.

Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy targeting both BCMA and CD38 induced an objective response in >90% of patients with multiple myeloma who had been treated with at least 3 prior therapies and whose disease had spread outside of the bone marrow.

Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy targeting both BCMA and CD38 induced an objective response in >90% of patients with multiple myeloma who had been treated with at least 3 prior therapies and whose disease had spread outside of the bone marrow.

Published: December 7th 2019 | Updated:

Published: December 5th 2020 | Updated:
Published: December 7th 2019 | Updated:

Published: February 20th 2020 | Updated:

Published: April 28th 2020 | Updated:

Published: June 11th 2021 | Updated: