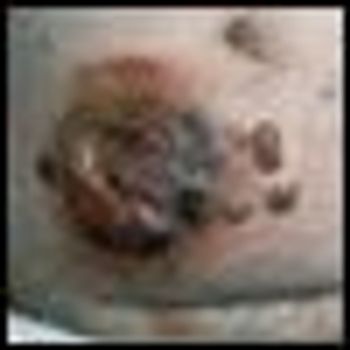
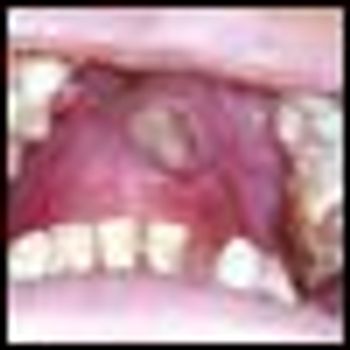
Mycosis fungoides (MF), the most common cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, is a low-grade cutaneous lymphoma characterized by skin-homing CD4+ T cells. It is notable for highly symptomatic progressive skin lesions, including patches, plaques, tumors, and erytheroderma, and has a poorer prognosis at later stages. Diagnosis remains difficult owing to MF’s nonspecific skin presentation and identification of the optimal treatment strategy is challenging given the paucity of controlled trials and numerous and emerging treatment options. Management includes topical therapy with the addition of systemic therapy for patients with later-stage disease including tumors; erythroderma; and nodal, visceral, or blood involvement. Topical therapies include mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard), carmustine (BCNU), steroids, bexarotene gel (Targretin Gel), psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA), ultraviolet B (UVB), and either localized or total skin electron radiotherapy. Systemic therapies include interferon, retinoids, oral bexarotene (Targretin), denileukin diftitox (Ontak), vorinostat (Zolinza), extracorporeal photochemotherapy (photopheresis), and cytotoxic chemotherapy. Herein, we outline clinically relevant aspects of MF, including clinical presentation, pathology, diagnosis, and staging. We describe in detail existing and emerging therapeutics and offer specific recommendations for management of each stage of MF.