
Pfizer's deal with the French company will ensure a market share in the promising immunooncology field.

Pfizer's deal with the French company will ensure a market share in the promising immunooncology field.
Opexa Therapeutics is initiating a phase IIb trial of a novel therapy that targets T-cells in patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis.

Ventana Medical Systems, Inc. and MedImmune today announced they are jointly developing a PD-L1 (SP263) immunohistochemistry assay to enroll patients in clinical trials for MedImmune's MEDI4736 anti-PD-L1 therapy for non-small cell lung carcinoma. This includes the recently commenced MEDI4736 ATLANTIC trial that will enroll only patients who express PD-L1 as determined by the VENTANA assay.

While seven drugs have been approved for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) since 2005, the most appropriate systemic therapy for non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (nccRCC) is unknown.

The addition of bevacizumab to erlotinib as first-line therapy yielded a significantly extended progression-free survival in patients with advanced EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to a new phase II study.

Two patients with metastatic cervical cancer achieved durable complete responses that have so far lasted from 15 to 22 months through an adoptive T-cell therapy (ACT) targeting the human papillomavirus (HPV) in a study that researchers say supports the concept that the experimental immunotherapy approach may be beneficial in a variety of tumor types.

An interview with Renier J. Brentjens, MD, PhD, on new therapies for patients with acute and chronic leukemias, in particular novel immunotherapies such as chimeric antigen receptor T cells.

A trial (NCT01582672) that will pair a targeted treatment with a vaccine therapy for firstline treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is recruiting at the Cedars-Sinai Samuel Oschin Comprehensive Cancer Institute.

Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Avalanche Biotechnologies announced a collaboration to discover, develop, and commercialize novel gene therapy products for the treatment of ophthalmologic diseases.

Patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with hyperfractionated radiation therapy (HFX) experienced improved local-regional control and, with patients censored at five years, improved overall survival with no increase in late toxicity.

Locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains a challenging disease to treat, with a 5-year survival rate for patients with unresectable stage III disease of approximately 20%, even after definitive radiation therapy and concurrent chemotherapy.

Technical advances in radiotherapy (RT), especially stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy (SABR), have allowed many non–small-cell lung cancer patients once considered untreatable to be eligible for locally effective therapies. Some patients will experience recurrence or will present with multiple lung primaries. We review the success and impact of SABR in patients who have undergone multiple course therapy.

Previous data from our institution suggest that imaging evidence of extracapsular extension, identified on pretreatment CT scans, independently predicts for worse distant control and survival for oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer (OPC) patients undergoing radiation therapy. In this present study, we sought to validate these findings in non-OPC head and neck squamous cell cancers.

An unmet clinical need in breast cancer (BC) management is the identification of which patients will respond to radiation therapy (RT). We hypothesized that the integration of post-RT clonogenic survival data with gene expression data across a large spectrum of BC cell lines would generate a BC-specific RT sensitivity signature predictive for RT response in BC patients and allow identification of patients with tumors refractive to conventional therapy.

Advances in intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) head and neck target delineation and treatment planning have led to improved sparing of organs at risk (OARs). In this study, we compare three IMRT techniques for the treatment of common cases of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.

This study examined circulating tumor cell (CTC) counts as measured by a novel EpCAM-independent assay and compared CTC counts with multiple known patient and tumor prognostic factors to determine the utility of pretreatment CTC levels as a preliminary prognostic biomarker for patients undergoing definitive radiation therapy (RT) for NSCLC.

Despite the success of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) as a treatment modality for early-stage non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), some patients develop localized intrathoracic recurrences after treatment. Effective salvage therapy for these patients has typically been limited. We examine our institutional experience using SBRT for salvage of intrathoracic recurrence after definitive SBRT for early-stage NSCLC.

Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) has become the treatment of choice for early-stage non–small-cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) in nonoperative candidates. The purpose of this study was to examine the efficacy and toxicity of SBRT for stage T2 NSCLC.

In patients with non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), there are few established predictors of outcomes. Pretreatment maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) has recently been debated as a prognosticator of progression-free survival (PFS). Here, we present a retrospective series with up to 86 months follow-up evaluating potential prognosticators of outcomes.

Five early-phase clinical trials exploring chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy have been suspended temporarily in response to the deaths of 2 patients with adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia

In a phase I trial, non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with tumors that expressed PD-L1 had significantly better outcomes with MK-3475 therapy compared with patients with PD-L1–negative tumors.

The effectiveness of radiation treatments for patients with squamous cell cancer of the head and neck has been reviewed by an international team of researchers. They identified two biomarkers that were good at predicting a patient's resistance to radiation therapy. "While our findings are encouraging, and a step toward personalized medicine, we hope to do more of this research with a larger, randomized trial," the authors conclude.

A retrospective study has shown that two targeted therapy drugs achieved similar outcomes among people with metastatic or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring an EGFR mutation.

Advances in treating multiple myeloma have transformed the field over the past decade, giving clinicians more effective therapy options for newly diagnosed patients who are candidates for stem cell transplant and those who are not.
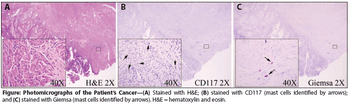
A 71-year-old woman not on hormone replacement therapy presented with uterine bleeding. Dilation and curettage revealed complex hyperplasia with atypia, focal clear-cell features, and endocervicitis. Endometrial intraepithelial carcinoma was suspected.

Scientists have successfully engineered platelet cells in dogs to express higher levels of factor VIII, paving the way for further tests in humans.
The order of the sequencing of sorafenib and sunitinib for first-line and second-line therapy did not affect progression-free and overall survival for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.


In the future, we also need to improve our ability to personalize the duration of endocrine therapy, with a goal of optimizing patient selection for extended therapy. Hopefully, clinical-pathologic indices and predictive biomarkers similar to the Oncotype DX 12-gene recurrence score or the PAM50 risk of recurrence score for adjuvant chemotherapy will soon emerge to guide adjuvant endocrine therapy.

To gain insight into the studies being presented at the ASH Annual Meeting, we interviewed Marcel R.M. van den Brink, MD, PhD, on abstracts being presented by faculty at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center.