
Within 4 months of the last reported incident, Juno Therapeutics has again halted the phase 2 “Rocket” trial of JCAR015 in patients with relapsed or refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).

Within 4 months of the last reported incident, Juno Therapeutics has again halted the phase 2 “Rocket” trial of JCAR015 in patients with relapsed or refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).

Treatment with recombinant adeno-associated virus vector gene-therapy was shown to be safe and potentially effective in a small test group of patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in record time has approved nivolumab (Opdivo) for the treatment of patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) with disease progression on or after a platinum-based therapy.

Individualizing frontline therapy for patients with non–small cell lung cancer based on preferences and clinical experience, as well as efficacy and safety data from pivotal trials, is an appropriate method for selecting EGFR-targeted agents.

Brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) has received an FDA breakthrough therapy designation for the treatment of patients with CD30-positive mycosis fungoides or primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma following at least 1 prior systemic therapy.

The FDA has approved nivolumab for patients with metastatic or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck following progression on platinum-based therapy.

A small study found that patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) who discontinue nivolumab due to immune-related adverse events can continue to derive benefit even after cessation of therapy.

Neoadjuvant therapy is evolving as a treatment approach for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.

Lajos Pusztai, MD, DPhil, discusses findings that suggest it is unlikely that any single gene can predict response to targeted therapy for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.

The treatment paradigm of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has been rapidly changing. First, the FDA approved the combination of lenvatinib and everolimus in May 2016 as a treatment for patients with advanced RCC following prior antiangiogenic therapy.
Although there are no drugs that target TP53 mutations in any tumor type, a recent analysis of a non–small cell lung cancer sample set raises the prospect that a more detailed understanding of this aberration eventually could help direct therapy.
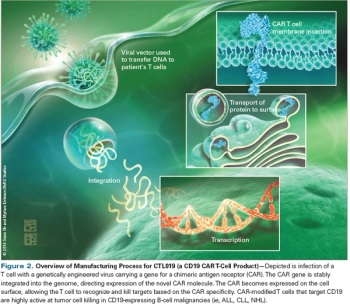
In this review, we will describe the mechanism of action of CAR T cells, discuss outcomes of current clinical trials, and highlight emerging directions for this exciting approach to cancer treatment.

In this interview we discuss the CRISPR technology currently being used to “edit” genes and when we might see the technology in mainstream practice.

Longer durations of maintenance therapy with lenalidomide were associated with longer survival among patients who underwent autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant for multiple myeloma.

First-line therapy with nivolumab failed to improve progression-free survival in PD-L1 positive non-small cell lung cancer compared with standard chemotherapy.

It turns out that CAR T cells can do more than directly attack cancer cells. They can be used as “micro-pharmacies” for precise therapeutic delivery in B-cell lymphomas.

The FDA has granted a breakthrough therapy designation to alectinib (Alecensa) as a frontline treatment for patients with ALK-positive non–small cell lung cancer.

Historically, patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma have had few treatment options, but several targeted agents and one immunotherapy, the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab, have been approved within the past 5 years, considerably expanding the RCC treatment arsenal. In the frontline setting, targeted agents are often the go-to therapy.

The preferred primary therapy for patients with multiple myeloma is induction therapy with a triplet regimen followed by autologous stem cell transplantation, consolidation, and maintenance.

Use of stereotactic body radiation therapy improved survival in elderly patients diagnosed with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer by about 20% over a decade.

The study in BMJ found that people with the FTO gene were just as likely to lose weight through interventions, such as diet, exercise, or therapy.

Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy targeting CD19 demonstrated a nearly 80% complete remission rate across relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients with multiple levels of disease burden.

The European Commission has approved lenvatinib (Kisplyx) in combination with everolimus for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma following 1 prior VEGF-targeted therapy.

The European Commission has approved cabozantinib for the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma after the failure of VEGF-targeted therapy, according to Exelixis and Ipsen, the manufacturers of the multikinase inhibitor.

Chimeric antigen receptor T-cells offer highly effective therapy for patients with minimal residual disease or bulky disease in both aggressive and indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas.

Evidence has demonstrated that obesity is a risk factor for clear cell renal cell carcinoma; however, a new report suggests that a high body mass index is a prognostic factor for improved survival in patients with metastatic RCC who have received targeted therapy.

An early-phase, dose-finding study using a defined composition of chimeric antigen receptor-T cells, in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, shows promise.

Investigators in Pittsburgh are now reporting it may be possible to delivery gene therapy to cancer patients in an entirely new way. Instead of using viruses as vehicles, it may be possible to use ultrasound energy.

Reducing barriers to hematopoetic stem cell (HPC) transplant is critical to supporting patients with one of the more than 70 blood cancers and other blood disorders (such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myloplastic dysplasia) for which a transplant may be the only therapy remaining with curative intent.

Patients with renal cancer who underwent cytoreductive nephrectomy and targeted therapy had improved survival compared with patients who did not undergo the surgery.