
German health authorities are debating whether the price of Europe's first approved gene therapy is worth the $1 million price tag.

German health authorities are debating whether the price of Europe's first approved gene therapy is worth the $1 million price tag.

For women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, the decision to undergo adjuvant chemotherapy following endocrine therapy has important implications to health and well-being. Now, a gene signature assay may help clinicians make more precise recommendations and there are new guidelines to reflect that.

Our institutional experience confirmed that SBRT to primary NSCLC is well tolerated and provides excellent LC, regardless of tumor size or histology. Tumor density did not appear to have a significant effect on PTC, but denser tumors were more likely to have poorer outcomes, likely owing to associated larger tumor burden.

Cetuximab may be considered as an alternative to cisplatin with concurrent RT, particularly for patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma who are not candidates for platinum therapy. These results indicate no difference in patterns of local or distant failure between cetuximab, low-dose weekly cisplatin, or q3 weekly high-dose cisplatin in this patient population.

The use of SBRT for T2bN0 primary NSCLC is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated treatment.

Delays to adjuvant RT > 60 days increased mortality by 17% to 35% compared to patients treated earlier. Current efforts should be focused on timely delivery of care, and further investigation into factors associated with delays is necessary.

Stem cell therapy is in its infancy, and the first steps have been taken to address atrophic age-related macular degeneration (AMD) with some success among several interesting treatment strategies, according to Allen C. Ho, MD.

The chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy JCAR017 elicited a 91% complete remission rate in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia.

The FDA has granted a breakthrough therapy designation to crizotinib as a potential treatment for patients with ROS1-positive non–small cell lung cancer.

Researchers are now reporting that the loss of a key gene (WAVE1) appears to be linked to a lethal form of prostate cancer.

The FDA has granted a priority review to the antibody-drug conjugate brentuximab vedotin as a consolidation therapy following autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma at risk of relapse or progression.

Infusions of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes from healthy donors led to high response rates and significant extensions in overall survival for patients with rituximab-refractory EBV–associated lymphoproliferative disorders.
Osteoarthritis (OA) patients may have an effective new treatment to look forward to following the development of self-donated fat cell therapy.

Gene therapy can provide transformative disease-modifying effects, with potentially lifelong clinical benefits after a single therapeutic administration. The most advanced retinal gene therapy program in the United States is in phase III study.
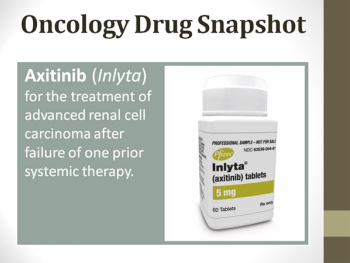
This oncology drug snapshot takes a look at axitinib (Inlyta) for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after failure of one prior systemic therapy.
Stem cell therapy for multiple sclerosis is effective at 3-year follow up, according to research published in JAMA Neurology.

Low pre-surgery uptake of a labeled glucose analogue, a marker of metabolic activity, in the primary tumor of patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer is associated with increased overall survival and a longer time before tumor recurrence, a study shows. Patients with high labeled glucose uptake may benefit from additional therapy following surgery.

A gene therapy treatment for men with hemophilia B proved effective, and the researchers involved in the study estimate it saved $2.5 million for the trial's patients.

The study, published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, found that patients treated with definitive concurrent chemotherapy and radiation therapy for stage 3 non-small cell lung cancer have longer overall survival when treated by highly experienced facilities, either academic or community cancer centers.

Inherited variants in an androgen transporter gene may determine the time to progression (TTP) for men with prostate cancer receiving androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).
Researchers have shown that reprogramming T cells to target glioblastoma in mice resulted in control of these tumors.

Neither sunitinib nor sorafenib reduced disease recurrence in patients with locally advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) when these agents were given to patients as adjuvant therapy, according to the results of a new study.

Genetic testing in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and subsequent molecular biomarker guided therapy is societally cost-effective compared to a chemotherapy treatment approach without molecular testing.
Patients with multiple sclerosis who received stem cell therapy instead of treatment with mitoxantrone achieved better outcomes over a 4-year-period.

Scientists are testing alternative therapeutic approaches that may delay disease progression and even protect and regenerate neurons.

An investigational cancer immunotherapy known as MPDL3280A (anti-PDL1) is receiving a breakthrough therapy designation from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

For his efforts to prove that gene therapy could one day provide lasting control of IOP in patients with glaucoma with known genetic defects, Andras M. Komáromy, PhD, DVM, was awarded the 2015 Shaffer Prize for Innovative Glaucoma Research.

The anti–PD-L1 agent MPDL3280A has received a breakthrough therapy designation from the FDA for PD-L1–positive non–small cell lung cancer that has progressed during or after platinum-based chemotherapy, as well as a targeted therapy for patients with EGFR- or ALK-positive tumors.
With 8 therapies approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), practitioners are faced with the challenge of selecting the most appropriate therapies for their patients within this crowded therapeutic landscape.

Wile several big and small pharmaceutical companies have invested research efforts in developing these complex, and expensive, treatment regimens, early results from trials indicate safety issues.