
Babis Andreadis, MD, discusses the successes seen with CAR T-cell development in the past year and the use of CAR T-cell therapy in patients with NHL.

Babis Andreadis, MD, discusses the successes seen with CAR T-cell development in the past year and the use of CAR T-cell therapy in patients with NHL.

In 2018, uniQure N.V. expects to advance the clinical development of AMT-130, its investigational gene therapy for the treatment of Huntington’s disease.

The FDA has granted a priority review to the CAR T-cell therapy tisagenlecleucel for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who are ineligible for or relapse after autologous stem cell transplant.

Researchers at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital have developed a new gene therapy that creates fully-functioning immune systems in babies diagnosed with severe combined immunodeficiency, commonly referred to as the “Bubble Boy” disease.
Why healthy adults should still get the flu vaccine; President Donald Trump undergoes first medical checkup of his presidency; review of Luxturna finds the $850,000 gene therapy needs a price discount.

The combination of the CAR T-cell therapy axicabtagene ciloleucel and the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab was highly active with a manageable safety profile in patients with refractory DLBCL enrolled in the phase I/II ZUMA-6 trial.

Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation showed long-lasting and consistent effects on opioid tolerance and opioid-induced hyperalgesia in rat and mouse models.

At the 36th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference, uniQure announced that in 2018, the company intends to advance its gene therapy AMT-061 into a pivotal study for hemophilia B.

Eisai’s multiple receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor lenvatinib and Merck’s anti–PD-1 therapy pembrolizumab as a combination therapy for patients with renal cell carcinoma received the designation based on results from the renal cell carcinoma cohort in Study 111.

BioMarin Chief Executive Officer Jean-Jacques Bienaime spoke about the company’s development of valoctocogene roxaparvovec, a gene therapy in development for the treatment of Hemophilia A.

The FDA has granted the combination of the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab and the VEGF/FGF inhibitor lenvatinib a breakthrough therapy designation for the treatment of patients with advanced and/or metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. was granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for voxelotor for the treatment of sickle cell disease.

Last week, Pfizer announced a new partnership with Sangamo. As part of the agreement, the sides will team to develop a potential gene therapy to treat ALS, or Lou Gehrig’s disease.
While chemotherapy with thoracic radiation has been established as the standard of care for the initial treatment of non-metastatic small-cell lung cancer, a large proportion of patients do not receive these treatments and in turn have lower overall survival, according to a study published in JAMA Oncology.

Recent data have found that the same gene editing platform can disable the defective gene responsible for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in mice. The therapy, which extended the lifespan of the mouse models by 25%, delayed the onset of the muscle wasting which characterizes the disease.

Spark Therapeutics CEO Jeff Marrazzo reassured patients and the medical community he has an obligation to ensure access to the novel gene therapy.
New vision loss gene therapy gets a price tag below the expected $1 million mark; new evidence finds that the prevalence of autism spectrum disorders has plateaued; hospitals are ill-equipped to care for dementia patients, but a new effort could change that.

Plinabulin, an antineoplastic agent that activates an immune response, is being investigated as a treatment option for patients with advanced or metastatic non–small cell lung cancer who have progressed after standard-of-care therapy.

The FDA has expanded the label for cabozantinib (Cabometyx) to include first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma regardless of treatment status. Cabozantinib was initially approved in patients who had previously received anti-angiogenic therapy.

Sagus Sampath, MD, discusses ongoing studies exploring checkpoint inhibitors with radiation therapy and the promise of integrating these 2 treatments in the field of non-small cell lung cancer.

The FDA has granted the PD-L1 inhibitor avelumab a breakthrough therapy designation for use in combination with the VEGF inhibitor axitinib in treatment-naïve patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.

The combination therapy increased the attraction of immune cells to fight non-small cell lung cancer and also boosted the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.

Universal gene expression profiling of patients with stage II breast cancer resulted in outpatient savings of $11,000 (inclusive of testing costs) within 6 months of initiation of medical therapy.

CAR T cells targeting CD19 can be effective at treating relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma or follicular lymphoma, with high rates of durable remission.
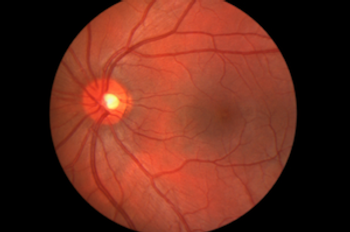
The FDA approved Spark Therapeutics Inc.’s voretigene neparvovec-rzyl (Luxturna), the first gene therapy for inherited vision loss caused by faulty gene mutations.

Ghassan K. Abou-Alfa, MD, discusses what he sees coming down the pike in epatocellular carcinoma with regard to novel agents, including CAR T-cell therapy, and the burgeoning questions with optimal sequencing of these treatments.

This is the first gene therapy approved in the US targeting mutations in a specific gene.

Every week, The American Journal of Managed Care® recaps the top managed care news of the week, and you can now listen to it on our podcast, Managed Care Cast.

Marcela V. Maus, MD, PhD, evaluates the next generation of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in both hematologic malignancies and solid tumors

Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells have hit prime time, with the 2 recent FDA approvals for this class of cell-based therapy.